In an increasingly connected world, speech technology plays a vital role in bridging communication gaps across languages and cultures. Yet, despite rapid progress in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), most commercial systems still cater to only a few dozen major languages. Billions of people who speak lesser-known or low-resource languages remain excluded from the benefits of modern AI voice systems.
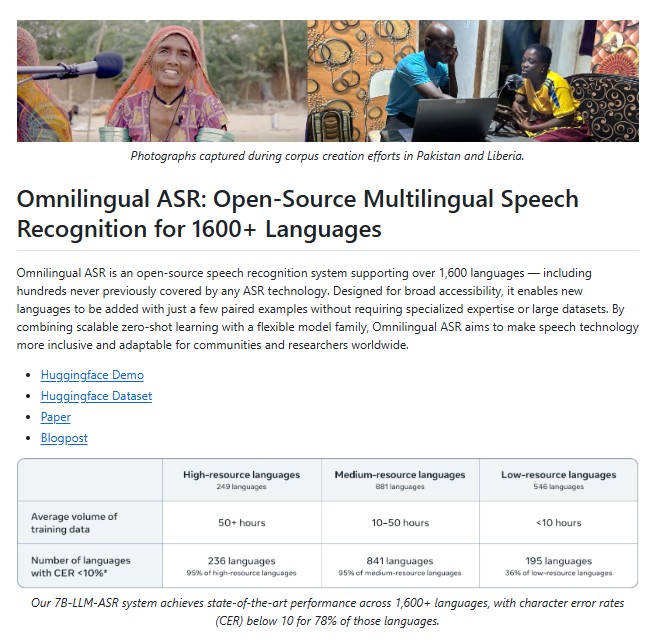
To change this, Meta’s FAIR (Fundamental AI Research) team has introduced Omnilingual ASR, an open-source, multilingual speech recognition model that supports over 1,600 languages including hundreds that have never before been covered by any ASR technology. This innovation sets a new standard for inclusivity, accessibility and open research in the field of multilingual AI.
Omnilingual ASR not only democratizes voice technology but also redefines what’s possible for zero-shot learning, low-resource language modeling, and global accessibility in speech AI.
What Is Omnilingual ASR?
Omnilingual ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) is an open-source multilingual system capable of understanding and transcribing speech in more than 1,600 languages. It was designed with a focus on scalability, inclusivity and ease of adaptation. The model can be fine-tuned or extended to new languages using just a few paired audio-text samples eliminating the need for massive datasets or advanced linguistic expertise.
Developed using Meta’s fairseq2 toolkit, Omnilingual ASR provides both a research framework and a ready-to-use inference pipeline. Its modular architecture combines self-supervised learning (SSL), Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) and Large Language Model (LLM)-based ASR techniques, creating a flexible and scalable solution for multilingual speech recognition.
A New Era of Global Speech Accessibility
The world has more than 7,000 spoken languages, yet most ASR systems support fewer than 100. This imbalance creates a digital divide, where technology favors speakers of dominant languages. Meta’s Omnilingual ASR directly addresses this issue by introducing the largest open multilingual ASR coverage ever achieved, covering more than 1,600 languages and dialects.
The system’s inclusive design makes it possible to develop accurate speech models even for low-resource or endangered languages, many of which lack sufficient data for conventional training methods.
Its zero-shot learning capabilities allow it to generalize to unseen languages, enabling instant transcription with minimal data — a breakthrough that could empower researchers, linguists and developers in regions historically underrepresented in AI research.
Key Features of Omnilingual ASR
1. Massive Language Coverage
Omnilingual ASR currently supports over 1,600 languages from English and Mandarin to languages like Ligurian, Swahili, and Bambara. This includes hundreds of languages that have never been represented in speech technology before.
The model’s structure follows a format like eng_Latn (English in Latin script) or cmn_Hans (Mandarin in Simplified Chinese), ensuring compatibility with multilingual datasets and linguistic diversity.
2. State-of-the-Art Accuracy
The flagship model, omniASR_LLM_7B, achieves character error rates (CER) below 10 for nearly 78% of the supported languages, a remarkable result considering the diversity of phonetics and linguistic structures involved.
This makes it the first large-scale ASR system to achieve near-human transcription accuracy across hundreds of previously unsupported languages.
3. Open Source and Accessible
Omnilingual ASR is released under the Apache 2.0 License, ensuring that developers, researchers, and institutions worldwide can access, modify, and integrate it freely.
The repository provides everything needed from setup and inference scripts to data preparation recipes — allowing both experts and beginners to get started effortlessly.
4. Flexible Architecture and Models
Omnilingual ASR includes multiple model families tailored for different needs:
- SSL (Self-Supervised Learning) models such as omniASR_W2V_300M to 7B
- CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification) models for efficient ASR training
- LLM-based ASR models that incorporate language conditioning for more context-aware transcription
Each model varies in size, parameters, and performance, with the 7B models offering near real-time transcription capabilities on modern GPUs.
5. Zero-Shot Learning for New Languages
Perhaps the most groundbreaking feature is its zero-shot learning capability. By leveraging multilingual embeddings and cross-lingual transfer, Omnilingual ASR can adapt to new languages or dialects with minimal labeled data. This drastically lowers the barrier to entry for expanding speech recognition coverage globally.
How Omnilingual ASR Works ?
The system integrates several powerful AI components into a unified inference pipeline. Here’s how it functions:
- Audio Input: The model accepts .wav or .flac files up to 40 seconds in length (with plans to extend this limit).
- Language Conditioning: Users specify the target language code (e.g., eng_Latn or deu_Latn).
- Feature Extraction: The pipeline applies wav2vec2-based feature extraction to process raw audio into contextual embeddings.
- Transcription: The embeddings pass through CTC or LLM layers to generate precise, time-aligned text transcriptions.
- Output: The final output is a text transcription that captures linguistic nuances, tone, and phrasing accurately.
Here’s an example of how to run inference:
from omnilingual_asr.models.inference.pipeline import ASRInferencePipeline pipeline = ASRInferencePipeline(model_card="omniASR_LLM_7B") audio_files = ["/path/to/eng_audio.flac", "/path/to/deu_audio.wav"] languages = ["eng_Latn", "deu_Latn"] transcriptions = pipeline.transcribe(audio_files, lang=languages, batch_size=2)
This simplicity ensures that even non-experts can deploy multilingual ASR models on personal or research projects.
Datasets and Hugging Face Integration
To further promote openness, Meta has released the Omnilingual ASR Corpus on Hugging Face under the CC-BY-4.0 license. This large-scale dataset contains multilingual audio samples from diverse speakers worldwide and can be directly integrated with the inference pipeline.
Example usage:
from datasets import load_dataset
omni_dataset = load_dataset("facebook/omnilingual-asr-corpus", "lij_Latn", split="train", streaming=True)
This integration provides a seamless bridge between open data, open models, and open research.
Performance and Efficiency
Omnilingual ASR’s models range from lightweight 300M-parameter systems to large 7B-parameter variants. Despite their scale, they remain highly efficient, achieving real-time or faster-than-real-time transcription on modern GPUs.
Performance comparisons show that the 7B-parameter models offer the best balance between accuracy, speed, and multilingual adaptability, making them ideal for both research and production environments.
Real-World Impact and Applications
The potential applications of Omnilingual ASR are far-reaching:
- Education: Empowering multilingual classrooms with real-time transcription tools.
- Healthcare: Enabling patient-doctor communication in multiple languages.
- Media and Journalism: Transcribing interviews or reports in low-resource languages.
- Accessibility: Supporting people with hearing impairments through instant captioning.
- Cultural Preservation: Digitizing and transcribing endangered languages to preserve linguistic diversity.
By offering an open and adaptable framework, Meta’s Omnilingual ASR enables governments, NGOs, and developers to build language technologies for communities that have long been underrepresented.
Conclusion
Omnilingual ASR is more than just a technological breakthrough — it’s a global initiative toward linguistic inclusivity in AI. By supporting over 1,600 languages and enabling new ones to be added with minimal data, Meta’s system sets a new benchmark for accessible speech recognition.
Through its open-source release, integration with Hugging Face, and zero-shot capabilities, Omnilingual ASR empowers anyone to develop advanced, multilingual voice applications without expensive infrastructure or exclusive datasets.
In a world where language is identity, Omnilingual ASR stands as a testament to AI’s potential to unite, rather than divide, human communication.
Follow us for cutting-edge updates in AI & explore the world of LLMs, deep learning, NLP and AI agents with us.
Related Reads
- LEANN: The Bright Future of Lightweight, Private, and Scalable Vector Databases
- Reducing Hallucinations in Vision-Language Models: A Step Forward with VisAlign
- DeepEyesV2: The Next Leap Toward Agentic Multimodal Intelligence
- Agent-o-rama: The End-to-End Platform Transforming LLM Agent Development
- CALM: Revolutionizing Large Language Models with Continuous Autoregressive Learning

2 thoughts on “Omnilingual ASR: Meta’s Breakthrough in Multilingual Speech Recognition for 1600+ Languages”