The world of large language models (LLMs) has evolved rapidly, producing advanced systems capable of reasoning, problem-solving, and creative text generation. However, a persistent challenge has been balancing translation quality with reasoning ability. Most translation-enhanced models excel in linguistic diversity but falter in logical reasoning or coding tasks. Addressing this crucial gap, the research paper LLaMAX2: Your Translation-Enhanced Model Also Performs Well in Reasoning introduces Qwen3-XPlus, a groundbreaking model that blends multilingual translation power with exceptional reasoning capabilities.
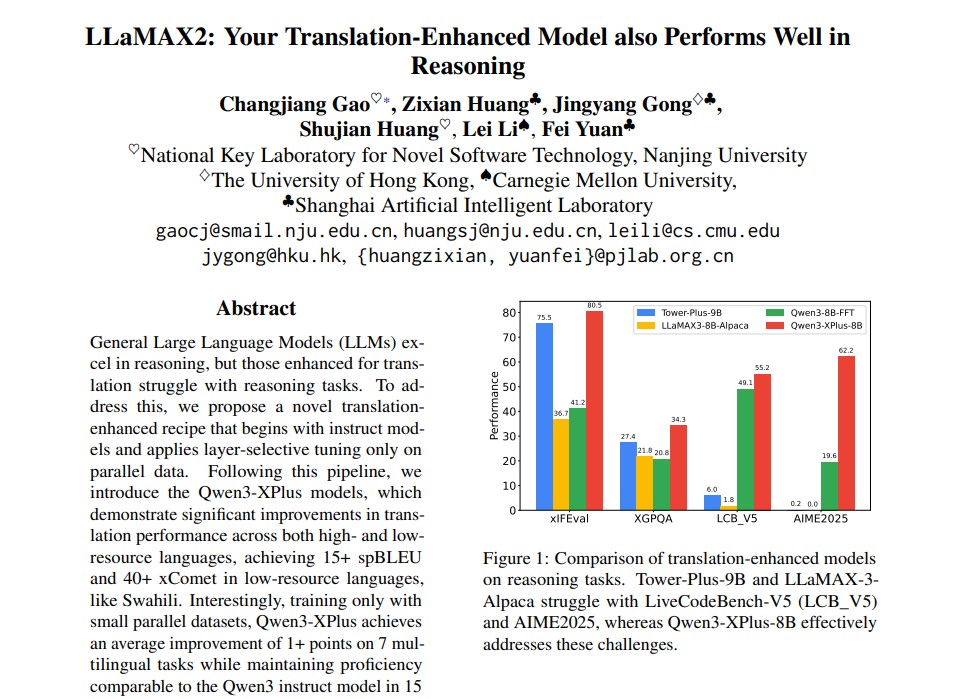
Developed through a collaboration between researchers from Nanjing University, the University of Hong Kong, Carnegie Mellon University and the Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, LLaMAX2 sets a new benchmark in multilingual model design. It challenges the traditional belief that models must compromise reasoning to gain translation proficiency.
The Challenge: Translation vs. Reasoning Trade-Off
Traditional large language models such as GPT, Claude and Gemini have demonstrated strong reasoning performance. In contrast, translation-optimized LLMs like Tower-Plus-9B or LLaMAX3 struggle with logical reasoning, code generation and mathematical problem-solving. This trade-off arises from the way these models are fine-tuned.
Conventional multilingual models often start from a base model and undergo full fine-tuning using massive multilingual datasets. While this improves translation accuracy, it causes catastrophic forgetting where the model loses prior reasoning abilities. This problem becomes worse with full-parameter training leading to performance degradation on non-translation tasks.
LLaMAX2 breaks this paradigm through a new approach that maintains balance between translation and reasoning.
The Breakthrough: Layer-Selective Tuning
The core innovation behind Qwen3-XPlus lies in its layer-selective tuning strategy. Instead of retraining all parameters, the model fine-tunes only selected layers using a small amount of parallel translation data. This approach preserves the model’s reasoning foundation while enhancing its multilingual performance.
The process follows a two-stage training pipeline:
- Stage 1 – Bottom Layer Training: Fine-tuning the lower layers near the embedding space to improve linguistic understanding.
- Stage 2 – Top Layer Training: Refining the top layers responsible for language generation ensuring accurate and natural translations.
This dual-phase technique eliminates the need for massive datasets or full-parameter updates drastically reducing computational cost while preventing catastrophic forgetting.
Data Efficiency and Low-Resource Adaptation
One of the most impressive aspects of Qwen3-XPlus is its data efficiency. Competing models like Tower-Plus-9B or Hunyuan-MT require tens or even hundreds of billions of tokens to achieve reasonable translation accuracy. In contrast, Qwen3-XPlus uses only 0.8 billion tokens sourced and cleaned from the NLLB and OPUS-100 datasets.
The research team implemented a six-step data preparation pipeline, including:
- Data formatting and cleaning
- Language identification
- Deduplication using SimHash
- Quality estimation
- Instructional reformatting
This meticulous preprocessing ensures consistency, quality and balanced coverage across high and low-resource languages.
As a result, Qwen3-XPlus achieves 15+ spBLEU and 40+ xComet score improvements in low-resource languages like Swahili – a milestone that highlights the power of small, curated datasets when combined with smart training strategies.
Outstanding Multilingual and Reasoning Performance
According to evaluations on the FLORES-101, BenchMAX and LiveCodeBench-V5 benchmarks, Qwen3-XPlus-8B and 14B outperform previous models across multiple metrics:
- Translation Performance: Achieved top-tier xComet scores across 17 languages.
- Multilingual Understanding: Outperformed baseline models like Qwen3 and Aya-Expanse in 5 of 7 multilingual tasks.
- Reasoning Competence: Maintained near-identical performance to instruction-tuned Qwen3 models in reasoning benchmarks such as AIME2025, OlympiadBench and HumanEval.
This makes Qwen3-XPlus the first translation-enhanced model to excel in both translation and reasoning simultaneously.
Why Qwen3-XPlus Matters ?
- Efficiency Over Scale: Demonstrates that innovation in model architecture can outperform brute-force scaling.
- Multilingual Equity: Bridges the gap for low-resource languages by reducing reliance on massive data.
- Balanced AI Development: Opens the door to building AI systems that are both linguistically rich and logically capable.
- Open Source Availability: Both the code and model weights are publicly accessible on:
These resources enable researchers and developers worldwide to explore, adapt and extend the work further.
The Future of Translation-Reasoning Models
LLaMAX2 represents more than an incremental improvement – it’s a paradigm shift. By proving that translation-enhanced models can maintain reasoning power, it opens new research directions in multimodal and multilingual intelligence.
In the near future, we can expect models like Qwen3-XPlus to play vital roles in:
- Cross-lingual education and tutoring
- Global scientific collaboration
- AI-powered programming assistance
- Inclusive communication technologies
Moreover, the layer-selective tuning approach can be applied beyond translation to domains like code generation, summarization and dialogue systems offering a scalable path for specialized yet balanced AI models.
Conclusion
The development of LLaMAX2 and its Qwen3-XPlus models marks a major milestone in the evolution of large language models. It challenges long-standing assumptions about the trade-off between multilingualism and reasoning. Through efficient design, thoughtful tuning and open collaboration, the researchers have created a model that performs exceptionally well across translation, reasoning and multilingual benchmarks all while remaining accessible and resource-efficient.
In a world increasingly driven by cross-cultural communication and AI reasoning, LLaMAX2 stands as a blueprint for the future of balanced, intelligent and inclusive large language models.
Follow us for cutting-edge updates in AI & explore the world of LLMs, deep learning, NLP and AI agents with us.
Related Reads
- Granite-Speech-3.3-8B: IBM’s Next-Gen Speech-Language Model for Enterprise AI
- Thinking with Camera 2.0: A Powerful Multimodal Model for Camera-Centric Understanding and Generation
- Jio AI Classroom: Learn Artificial Intelligence for Free with Jio Institute & JioPC App
- Unsloth AI: The Game-Changer for Efficient 2*Faster LLM Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning
- Ultimate OpenTSLM: Stanford’s Open-Source Framework Bridging LLMs and Medical Time-Series Data

3 thoughts on “LLaMAX2 by Nanjing University, HKU, CMU & Shanghai AI Lab: A Breakthrough in Translation-Enhanced Reasoning Models”