Machine Learning models are powerful but building them is only half the story. The true challenge lies in deploying, scaling and maintaining these models in production environments – a process that requires collaboration between data scientists, developers and operations teams.
This is where MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) comes in. MLOps combines the principles of DevOps with machine learning workflows to automate and streamline the process from data collection to model deployment and monitoring.
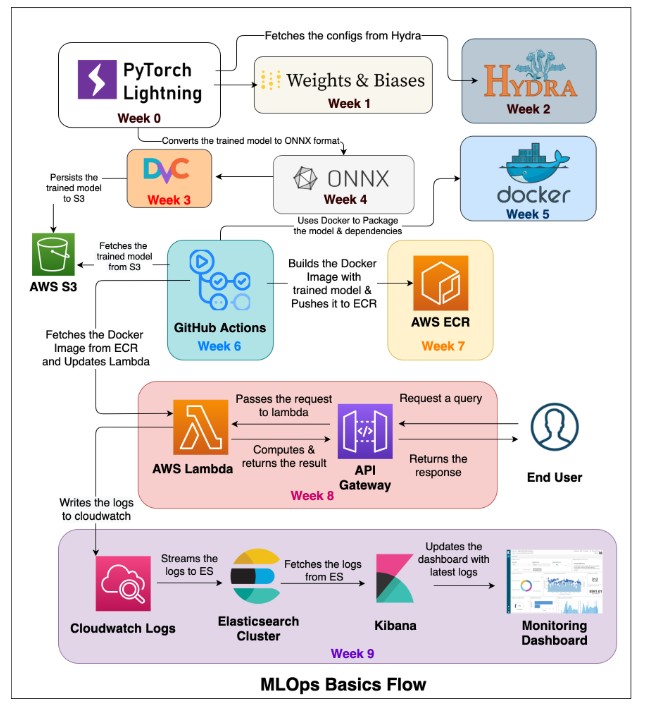
The open-source project “MLOps-Basics” by graviraja provides an excellent, hands-on approach to learning the core concepts of MLOps. Through a 10-week structured series, it covers every essential aspect from project setup and data versioning to CI/CD, serverless deployment and prediction monitoring.
If you’re looking to understand how to take a model from experimentation to production, this guide will walk you through the key lessons from the MLOps-Basics project.
Week 0: Project Setup
The journey starts with setting up a simple classification problem using the HuggingFace ecosystem. The project demonstrates how to collect and process data, define dataloaders, declare models and train them efficiently using PyTorch Lightning.
Key technologies:
- HuggingFace Datasets
- HuggingFace Transformers
- PyTorch Lightning
This stage ensures that your machine learning model is reproducible, modular and ready for experimentation laying the foundation for the rest of the MLOps pipeline.
Week 1: Model Monitoring with Weights & Biases
Once the model is built, tracking experiments becomes crucial. The project integrates Weights & Biases (W&B) for real-time tracking of metrics, hyperparameters and performance comparisons.
Through W&B dashboards, developers can visualize model performance, plot validation losses and log datasets helping them identify overfitting, data drift or training instability early.
Key takeaways:
- Log metrics and losses with W&B
- Track hyperparameter experiments
- Visualize results and data samples
- Monitor model improvements over time
Tech stack: Weights & Biases, TorchMetrics
Week 2: Configuration Management with Hydra
Managing configurations across multiple environments is a common challenge. Hydra helps organize and override configuration files easily.
In MLOps-Basics, Hydra is used to manage training parameters, data paths and model settings making it simple to run experiments with different configurations using a single command.
Topics covered:
- Basics of Hydra
- Splitting and overriding configurations
- Variable interpolation
- Running parameter combinations automatically
Tech stack: Hydra
Week 3: Data Version Control (DVC)
Traditional version control tools like Git struggle with large datasets and model files. This is where Data Version Control (DVC) comes in.
The project integrates DVC to track datasets, store model checkpoints and sync them with remote storage like AWS S3. This ensures full reproducibility of results even months after training.
Core concepts:
- Initializing DVC in a project
- Configuring remote storage (e.g., S3)
- Saving and versioning models
- Synchronizing data across teams
Tech stack: DVC
Week 4: Model Packaging with ONNX
Model packaging allows developers to run their trained models across various platforms and frameworks.
The project uses ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange) to convert PyTorch models into a format compatible with other environments. With ONNX Runtime, the packaged models can be deployed for high-performance inference on any device.
Covered topics:
- What is ONNX and why it matters
- Converting trained models to ONNX format
- Running inference with ONNX Runtime
- Comparing performance across environments
Tech stack: ONNX, ONNXRuntime
Week 5: Containerization with Docker
One of the biggest challenges in deployment is environment inconsistency what works on one system might fail on another. Docker solves this by packaging code, dependencies and configurations into a single portable container.
In this stage, the project shows how to:
- Create a FastAPI wrapper for serving models
- Build a Docker image for deployment
- Use Docker Compose for multi-container setups
Once containerized, your ML app can run reliably on any cloud platform, enabling scalability, reliability and faster deployment.
Tech stack: Docker, FastAPI
Week 6: Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) with GitHub Actions
Automation is at the heart of MLOps. The CI/CD pipeline ensures that every change whether in data, model or code is automatically tested, validated and deployed.
Using GitHub Actions, the project demonstrates how to automate the entire pipeline:
- Build and test your model automatically
- Use Google Service Accounts for authentication
- Deploy models with minimal manual intervention
This step establishes a fully automated, production-ready workflow.
Tech stack: GitHub Actions, DVC, Docker
Week 7: Container Registry with AWS ECR
To deploy Dockerized models, you need a reliable registry to store your container images. Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) serves this purpose.
This part of the project explains how to:
- Configure AWS S3 for remote storage
- Push and pull container images from ECR
- Automate image deployment with GitHub Actions
This ensures secure, scalable management of model containers in production environments.
Tech stack: AWS ECR, AWS S3, Docker
Week 8: Serverless Deployment with AWS Lambda
Serverless architectures simplify deployment by eliminating the need to manage servers manually.
Using AWS Lambda, the project deploys ML models as serverless functions. These functions automatically scale based on demand and can be triggered via API Gateway.
Developers also learn to automate deployment workflows to Lambda using GitHub Actions combining speed, scalability and cost efficiency.
Tech stack: AWS Lambda, API Gateway, Docker
Week 9: Model Monitoring with Kibana
After deployment, monitoring model predictions ensures that models remain reliable over time. The project concludes by integrating Kibana with Elasticsearch and CloudWatch for visualization and logging.
By monitoring logs and dashboards, developers can detect data drift, model decay and operational issues early helping trigger retraining or redeployment when necessary.
Tech stack: Kibana, Elasticsearch, CloudWatch
Conclusion
The MLOps-Basics project offers a practical, end-to-end roadmap for mastering the MLOps lifecycle. From model training to serverless deployment and continuous monitoring, it encapsulates everything you need to build production-ready machine learning systems.
By integrating tools like Hydra, DVC, Docker, GitHub Actions, AWS Lambda and Kibana, it demonstrates how to automate every stage of the ML workflow efficiently.
Whether you are a data scientist wanting to scale your experiments or an engineer aiming to operationalize models, MLOps-Basics provides the perfect foundation to bridge the gap between machine learning and production.
Follow us for cutting-edge updates in AI & explore the world of LLMs, deep learning, NLP and AI agents with us.
Related Reads
- Reflex: Build Full-Stack Web Apps in Pure Python — Fast, Flexible and Powerful
- Wren AI: Transforming Business Intelligence with Generative AI
- Google’s GenAI MCP Toolbox for Databases: Transforming AI-Powered Data Management
- Microsoft Data Formulator: Revolutionizing AI-Powered Data Visualization
- PandasAI: Transforming Data Analysis with Conversational Artificial Intelligence

2 thoughts on “MLOps Basics: A Complete Guide to Building, Deploying and Monitoring Machine Learning Models”