In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has made remarkable strides in transforming healthcare. From medical imaging to patient monitoring systems, AI-driven solutions are reshaping how clinicians diagnose, treat and manage diseases. One of the most promising developments in this space is the integration of large language models (LLMs) with time-series data, a combination that holds immense potential for improving healthcare outcomes.
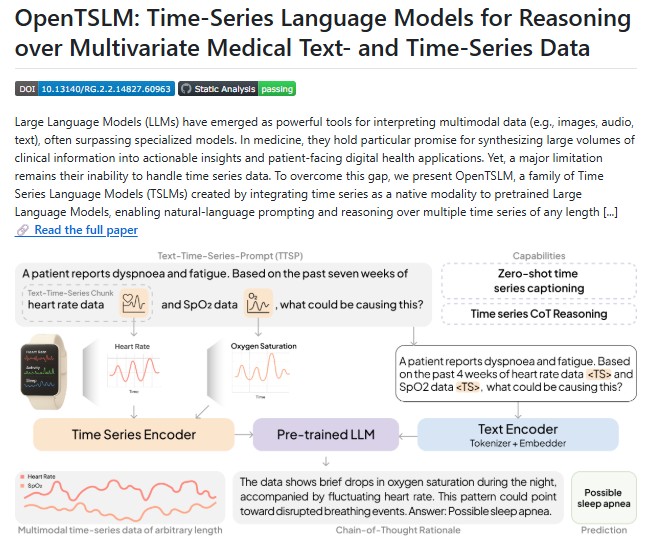
Enter OpenTSLM, a cutting-edge framework that enables reasoning over multivariate medical text and time-series data using LLMs marking a significant advancement in digital health research.
Understanding the Challenge: Time-Series Data in Healthcare
Healthcare data is inherently complex. Clinicians often rely on continuous streams of information, such as electrocardiograms (ECGs), electroencephalograms (EEGs) and wearable sensor readings which evolve over time. This time-series data provides critical insights into patient health but is notoriously difficult to analyze due to its sequential nature and high dimensionality. Traditional AI models, including standard LLMs, struggle to fully interpret these data streams limiting their application in real-world clinical scenarios.
While LLMs excel at understanding natural language, their inability to process time-series data natively has been a major limitation until now.
Introducing OpenTSLM
OpenTSLM (Open Time-Series Language Models) addresses this limitation by integrating time-series as a native modality within pretrained LLMs. Developed by a collaborative team of researchers from Stanford University, ETH Zurich, Google Research and other leading institutions, it is designed to interpret and reason over multiple time-series of any length. This capability opens doors for advanced applications in digital health, from real-time patient monitoring to clinical decision support.
By combining the reasoning capabilities of LLMs with the sequential understanding of time-series data, it allows researchers and clinicians to generate findings, rationales and detailed captions from complex medical datasets, something that was previously challenging or impossible with traditional models.
Key Features
Multimodal Reasoning
It can handle multiple streams of time-series data simultaneously, such as 12-lead ECGs, EEG sleep recordings and wearable sensor data. This makes it highly versatile for tasks like human activity recognition (HAR), sleep stage classification and ECG question answering.
Curriculum Learning for Progressive Training
To maximize model performance, it uses multi-stage curriculum learning. The training process is broken down into progressive stages, each building upon the previous one:
- Stage 1 (MCQ): Multiple-choice questions on time-series data.Stage 2 (Captioning): Generating descriptive captions for time-series sequences.Stage 3 (Chain-of-Thought – HAR): Reasoning on human activity recognition.Stage 4 (Sleep CoT): Chain-of-thought reasoning on EEG sleep stage classification.Stage 5 (ECG CoT): Chain-of-thought reasoning on ECG question answering.
Compatibility with Leading LLMs
It works seamlessly with Llama and Gemma models, including Meta’s Llama 3.2-1B and Google’s Gemma 3-270m, allowing users to leverage state-of-the-art language models without compromising on time-series reasoning capabilities.
Natural Language Outputs
One of the most innovative aspects of OpenTSLM is its ability to translate complex time-series patterns into human-readable text, such as diagnostic rationales, detailed captions and step-by-step reasoning. This makes it easier for clinicians to interpret AI-generated insights and integrate them into clinical workflows.
Open-Source and Accessible
It is available on GitHub, allowing researchers, students, and healthcare innovators to explore, contribute and extend its capabilities. With clear installation instructions and structured results organization, it’s designed to be user-friendly for both research and applied healthcare projects.
Applications in Healthcare
The potential applications of OpenTSLM in healthcare are vast:
- ECG Analysis: Automatically generate diagnostic insights from 12-lead ECGs reducing manual interpretation workload.
- Sleep Stage Classification: Analyze EEG data to identify sleep patterns and detect abnormalities.
- Human Activity Recognition: Leverage wearable sensors to monitor patient activity levels, useful for rehabilitation and chronic disease management.
- Time-Series Captioning: Produce interpretable summaries of complex physiological signals for research and clinical documentation.
By translating raw time-series data into meaningful narratives, it enhances decision-making reduces cognitive load for clinicians and accelerates research in digital health.
Why OpenTSLM Matters ?
Healthcare is increasingly data-driven, but raw data alone isn’t enough. The true value lies in interpreting data accurately and efficiently. OpenTSLM bridges the gap between raw time-series signals and actionable insights enabling precision medicine at scale.
Moreover, as telemedicine and remote patient monitoring become more prevalent, tools like OpenTSLM will be critical in analyzing continuous streams of patient data providing early warnings and guiding personalized treatment plans.
Getting Started
OpenTSLM is easy to deploy for those familiar with Python and AI frameworks. To get started:
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/StanfordBDHG/OpenTSLM.git --recurse-submodules
- Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Run training or evaluation with pre-trained LLMs, such as Llama or Gemma, using the provided curriculum_learning.py script.
Comprehensive instructions, supported models, and example workflows are detailed in the GitHub repository.
Conclusion
OpenTSLM represents a transformative step forward in AI-powered healthcare. By integrating time-series data with large language models, it empowers researchers and clinicians to extract actionable insights from complex medical signals. Whether it’s ECG analysis, sleep staging or human activity monitoring, it provides a robust, interpretable and accessible platform for next-generation digital health solutions.
As AI continues to evolve, frameworks like OpenTSLM will play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare where data-driven insights meet clinical expertise, enhancing patient outcomes and accelerating medical research.
Follow us for cutting-edge updates in AI & explore the world of LLMs, deep learning, NLP and AI agents with us.
Related Reads
- Quivr AI: Building Your Second Brain with Open-Source Generative Intelligence
- Top 20 Ultimate Bollywood Diwali Portrait Ideas for Women Using Gemini AI
- Try Powerful Mem0 AI to build Long-Term Memory for AI Agents
- Grok AI Chatbot (2025): Elon Musk’s Bold Answer to Real-Time, Intelligent Conversation
- Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach — The Ultimate Number 1 Guide to Learning AI by Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig

4 thoughts on “Ultimate OpenTSLM: Stanford’s Open-Source Framework Bridging LLMs and Medical Time-Series Data”