In an era where information is predominantly digital, the ability to extract, interpret and organize data from documents is crucial. From invoices and research papers to multilingual contracts and handwritten notes, document parsing stands at the intersection of vision and language. Traditional Optical Character Recognition (OCR) systems have made impressive strides but they often fall short when it comes to understanding complex layouts, diverse languages and structured data such as tables, formulas and charts.
To overcome these challenges, Baidu’s PaddlePaddle team has introduced PaddleOCR-VL, a state-of-the-art ultra-compact vision-language model that revolutionizes document parsing. Combining the visual power of the NaViT-style dynamic visual encoder and the linguistic intelligence of ERNIE-4.5-0.3B, PaddleOCR-VL sets a new benchmark for multilingual document understanding supporting 109 languages with unparalleled efficiency and accuracy.
What Is PaddleOCR-VL?
PaddleOCR-VL is a 0.9B-parameter vision-language model (VLM) optimized for multilingual document parsing. It bridges computer vision and natural language processing to achieve page-level and element-level document understanding recognizing not only text but also tables, formulas and charts within complex layouts.
Unlike heavy multimodal models that require enormous computational resources, PaddleOCR-VL achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance with minimal resource consumption. This makes it ideal for real-world deployments including enterprise document automation, data extraction and digital archiving.
Core Architecture: Compact Yet Powerful
At the heart of PaddleOCR-VL lies a two-stage architecture designed for both precision and efficiency:
- Layout Analysis with PP-DocLayoutV2
- This module handles layout detection and reading order prediction.
- Built on RT-DETR and enhanced with a pointer network, it identifies semantic regions (text, tables, figures) and predicts their logical reading order.
- This modular design ensures fast, stable and accurate layout recognition even in multi-column or mixed-language documents.
- Element-Level Recognition with PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B
- This stage performs deep recognition of document elements.
- The NaViT-style visual encoder processes images at dynamic resolutions, reducing distortion and hallucinations common in fixed-size models.
- The ERNIE-4.5-0.3B language model interprets the extracted features, generating structured outputs in Markdown or JSON formats.
Together, these modules form a lightweight yet robust pipeline for document understanding that’s both faster and more accurate than its competitors.
PaddleOCR Models on Hugging Face
PaddleOCR-VL Research Paper (arXiv:2510.14528v2)
High-Quality Data Construction Pipeline
PaddleOCR-VL’s excellence stems from its systematic data curation and training methodology. The Baidu team constructed over 30 million high-quality training samples, combining public datasets, synthetic data and in-house collections.
- Open-source data: Integrated from datasets like CASIA-HWDB for handwritten text and ChartQA for chart recognition.
- Synthetic data generation: Addressed data imbalance by generating missing or rare document types.
- Automated annotation: Used advanced multimodal models (ERNIE-4.5-VL and Qwen2.5-VL) to refine labels and remove hallucinated data.
- Hard case mining: Identified weak areas (e.g., complex tables or handwritten formulas) and generated challenging synthetic samples to enhance robustness.
This meticulous process ensures that PaddleOCR-VL performs reliably across diverse document types from scanned historical manuscripts to corporate reports.
Training and Optimization Strategy
The training process for PaddleOCR-VL is divided into two stages:
- Pretraining for Multimodal Alignment
The model learns associations between visual and textual features using 29 million image-text pairs. This stage builds foundational cross-modal understanding. - Instruction Fine-tuning
Using 2.7 million specialized samples, the model is fine-tuned on four core tasks:- OCR: Extracting text blocks, lines and characters.
- Table Recognition: Parsing tabular structures using OTSL format.
- Formula Recognition: Translating mathematical expressions into LaTeX.
- Chart Recognition: Converting visual data into Markdown tables.
This dual-phase training ensures that the model is both generalizable and task-optimized delivering consistent results across complex multilingual layouts.
Benchmark Results: Setting a New Standard
PaddleOCR-VL demonstrates remarkable performance on multiple public and in-house benchmarks:
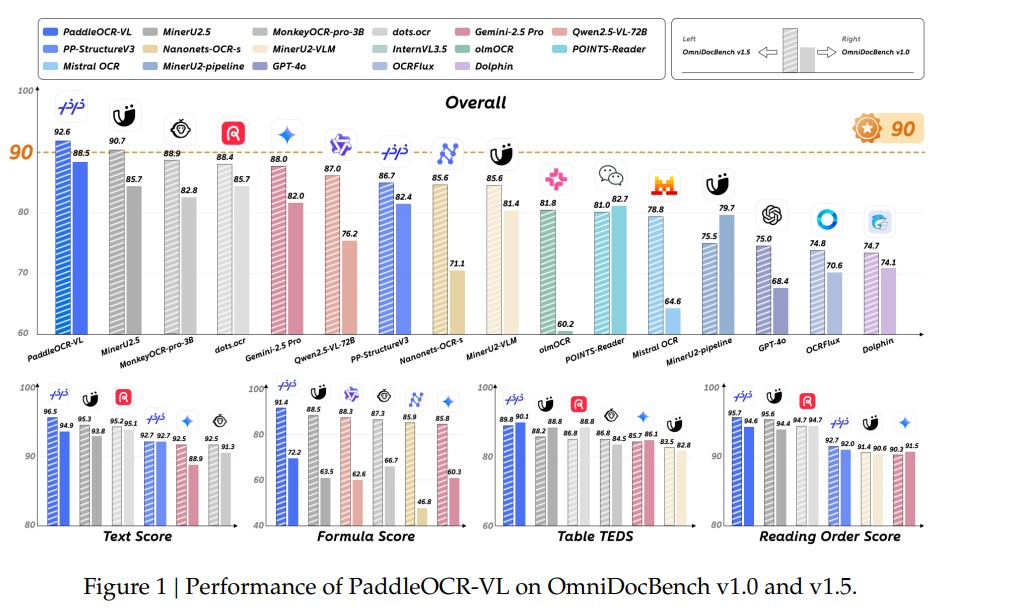
- OmniDocBench v1.5: Achieved the highest overall score of 92.56, outperforming top models like MinerU2.5 and MonkeyOCR.
- olmOCR-Bench: Scored 80.0 ± 1.0, surpassing GPT-4o, Gemini 2.5 Pro and other leading VLMs in real-world document tasks.
- Text Recognition: Outperformed all competitors in 109 languages with the lowest edit distances across handwritten and printed scripts.
- Table and Formula Recognition: Delivered the best TEDS (0.9195) and CDM (0.9882) scores, respectively, ensuring structural and semantic accuracy.
- Chart Understanding: Achieved an RMS-F1 score of 0.8440 exceeding larger multimodal models.
These benchmarks confirm PaddleOCR-VL’s dominance in both accuracy and efficiency making it one of the most practical VLMs for document processing to date.
Efficiency and Real-World Deployment
One of PaddleOCR-VL’s biggest strengths lies in its speed and resource efficiency. The model is optimized for asynchronous multi-threaded execution enabling concurrent data loading, layout detection and VLM inference.
- 15.8% higher page throughput than MinerU2.5.
- 40% lower GPU memory usage compared to dots.ocr.
- 1.22 pages per second processing rate on an NVIDIA A100 GPU.
These metrics highlight the model’s readiness for industrial-scale deployment from cloud-based OCR services to on-device document understanding applications.
Key Features
- Supports 109 Languages including English, Chinese, Arabic, Hindi, Tamil and Russian.
- Ultra-Compact Model (0.9B parameters) with SOTA accuracy.
- Two-Stage Parsing System separating layout analysis from content recognition.
- NaViT + ERNIE Fusion for powerful visual-textual reasoning.
- Structured Output in Markdown and JSON formats for easy integration.
- Specialized in Complex Elements like tables, charts and formulas.
- Optimized for Real-Time Inference with multi-threaded execution.
Conclusion
PaddleOCR-VL represents a significant milestone in the evolution of document parsing technology. Its combination of multilingual capability, compact design and state-of-the-art performance positions it as a next-generation solution for intelligent document understanding.
By bridging computer vision and natural language processing through an efficient multimodal framework, Baidu’s PaddleOCR-VL not only sets a new industry benchmark but also opens new avenues for AI-driven document automation, knowledge extraction and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications.
For developers, researchers and enterprises, PaddleOCR-VL is more than just an OCR tool – it’s a complete foundation model for multilingual document intelligence.
Follow us for cutting-edge updates in AI & explore the world of LLMs, deep learning, NLP and AI agents with us.
Related Reads
- NanoChat: The Best ChatGPT That $100 Can Buy
- Unleashing the Power of AI with Open Agent Builder: A Visual Workflow Tool for AI Agents
- Sora: OpenAI’s Breakthrough Text-to-Video Model Transforming Visual Creativity
- Agentic Entropy-Balanced Policy Optimization (AEPO): Balancing Exploration and Stability in Reinforcement Learning for Web Agents
- NVIDIA, MIT, HKU and Tsinghua University Introduce QeRL: A Powerful Quantum Leap in Reinforcement Learning for LLMs

1 thought on “PaddleOCR-VL: Redefining Multilingual Document Parsing with a 0.9B Vision-Language Model”