As Large Language Models (LLMs) continue to redefine artificial intelligence, a new research breakthrough has emerged from Meta, The University of Texas at Austin, University College London, UC Berkeley, Harvard University and Periodic Labs. Their paper, titled “The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs,” introduces a transformative framework for understanding how reinforcement learning (RL) can be scaled predictably and efficiently.
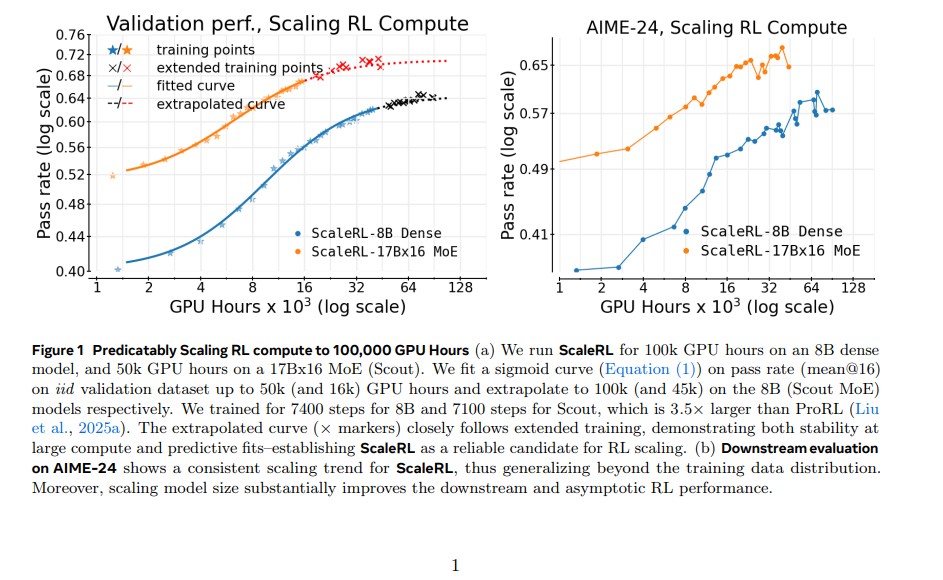
While pre-training has long benefited from well-established scaling laws, the RL phase responsible for fine-tuning LLMs to reason, act and adapt has remained somewhat of a mystery. This paper changes that providing the first scientific framework for scaling RL compute in LLMs.
Why Reinforcement Learning Matters for LLMs ?
Reinforcement Learning is at the heart of some of today’s most powerful AI models. It’s the stage where LLMs learn to think step-by-step, make decisions and improve through feedback.
For example, models like DeepSeek-R1-Zero devoted over 100,000 GPU hours to RL training, highlighting the massive computational investment behind advanced reasoning capabilities. Similarly, OpenAI’s GPT series and xAI’s Grok models have seen more than a 10x increase in RL compute from earlier to newer versions.
However, despite this explosion in compute usage, the field has lacked a clear, predictable scaling methodology. Developers and researchers have relied on trial-and-error approaches making RL scaling more of an art than a science until now.
Introducing ScaleRL: Predictable Scaling for Reinforcement Learning
The research introduces a groundbreaking framework named ScaleRL, a robust RL recipe that scales predictably with compute. Developed through over 400,000 GPU-hours of experiments, ScaleRL bridges the gap between empirical intuition and mathematical predictability.
At the core of this framework lies a sigmoidal compute-performance curve, a mathematical model that captures how performance improves with more computational investment. The formula allows researchers to extrapolate LLM performance from smaller-scale experiments reducing costs and accelerating innovation.
In essence, ScaleRL gives RL training the same predictability and consistency that pre-training already enjoys.
Key Insights from the Study
After extensive testing and ablation studies, the researchers uncovered several critical insights about RL scaling:
- RL Performance Ceilings Are Not Universal
Different algorithms reach different maximum performance levels (asymptotes). This means that design choices like loss type or batch size can shift the upper limits of model capability. - Bigger Isn’t Always Better – Efficiency Matters
Some methods that perform well on small compute budgets may underperform at scale. The paper refers to this as “embracing the bitter lesson” – the idea that scalable methods might initially seem less efficient but dominate when scaled. - Design Details Affect Efficiency, Not Capability
Elements such as normalization, data curriculum, and loss aggregation mainly improve compute efficiency rather than the final performance ceiling. - Predictive Scaling Is Possible
By fitting performance curves at small compute levels, researchers were able to accurately predict large-scale outcomes even for runs exceeding 100,000 GPU-hours.
What Makes ScaleRL Different ?
ScaleRL is not a completely new algorithm, it’s an optimized combination of existing best practices. The research team fine-tuned every aspect of the RL process to create a stable, predictable and efficient framework. Some standout features include:
- PipelineRL setup for asynchronous off-policy learning.
- Truncated importance sampling (CISPO) loss for robust optimization.
- FP32 precision at logits to eliminate numerical instability.
- Prompt-level loss averaging for balanced gradient updates.
- Zero-variance filtering and No-Positive-Resampling, which remove redundant prompts and improve learning efficiency.
Each component was tested in leave-one-out (LOO) experiments to confirm its impact on scalability and performance.
Scaling Reinforcement Learning Across Dimensions
The study didn’t stop at theoretical validation – it demonstrated predictable scaling across multiple training dimensions:
- Model Size: From 8B dense models to massive 17B×16 MoE architectures, ScaleRL maintained stability and predictable results.
- Context Length: Longer generation lengths (up to 32,768 tokens) produced higher final performance, validating long-context RL as a key scaling factor.
- Batch Size: Larger batch sizes improved both training stability and asymptotic performance.
- Multi-Task Training: ScaleRL generalized effectively across domains like math and code, showcasing its versatility.
Real-World Impact and Future Directions
This research sets a new precedent for scientific rigor in RL scaling. By offering a predictive and reproducible framework, ScaleRL empowers both industry and academia to optimize training efficiency without guesswork.
In practical terms, this means:
- Lower costs for RL experimentation by predicting outcomes early.
- Better utilization of GPU resources.
- Standardized metrics for comparing RL algorithms at different compute levels.
The authors also highlight future directions such as developing scaling laws that connect pre-training and RL phases, studying multi-turn RL and integrating reward modeling with generative verification systems.
Conclusion
The collaboration between Meta, UT Austin, Harvard, UCL, UC Berkeley and Periodic Labs marks a significant leap forward in AI research. Their work, “The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs,” transforms RL from an unpredictable art into a measurable science.
By establishing the ScaleRL framework, the researchers have provided the AI community with a tool to forecast performance, reduce training waste and push the limits of reasoning models. This advancement not only accelerates LLM development but also brings us one step closer to a future where AI training is both efficient and predictable.
Follow us for cutting-edge updates in AI & explore the world of LLMs, deep learning, NLP and AI agents with us.
Related Reads
- DeepSeek-OCR: Redefining Document Understanding Through Optical Context Compression
- Wan 2.1: Alibaba’s Open-Source Revolution in Video Generation
- Top 30 More Retro Bollywood Diwali Portrait Prompts for Women Using Gemini AI – Part 2
- PaddleOCR-VL: Redefining Multilingual Document Parsing with a 0.9B Vision-Language Model
- NanoChat: The Best ChatGPT That $100 Can Buy

2 thoughts on “The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs: Top Insights from Meta, UT Austin & Harvard University”